If you’ve ever traveled by train, you’ve likely noticed the endless rows of crushed stones lining the railway tracks. While they may appear to be nothing more than scattered gravel, these stones serve a crucial function in ensuring the stability and safety of rail transport. These crushed stones, known as track ballast, play a vital role in maintaining the integrity of the railway infrastructure.
What is Track Ballast?
Track ballast forms the foundation upon which railway sleepers (or ties) are laid. These stones are carefully selected and strategically placed below, between, and around the sleepers to provide essential structural support. The thickness of track ballast generally ranges between 25-30 cm, depending on geographic and environmental conditions. Typically, ballast consists of crushed stones such as granite, limestone, or basalt, though alternatives like burnt clay have been used in some cases.
However, not just any type of stone can serve as ballast. The stones must have sharp, angular edges to ensure they interlock effectively. Smooth or rounded stones would slide over each other, compromising the stability of the track, which could lead to severe safety hazards.
Why Are There Stones Along Railway Tracks?
There are several essential reasons for the presence of track ballast. These include:
1. Holding the Sleepers in Place
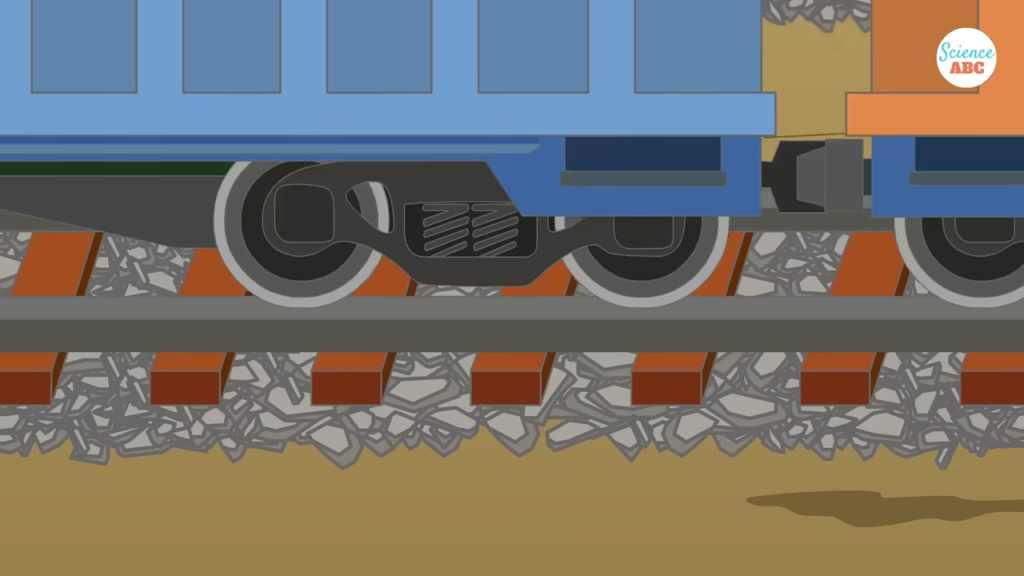
Trains exert enormous pressure on railway tracks. Without ballast, the sleepers could shift longitudinally or laterally, weakening the track structure. The ballast ensures that the sleepers remain firmly in place, distributing the train’s weight evenly.
2. Distributing Load Evenly
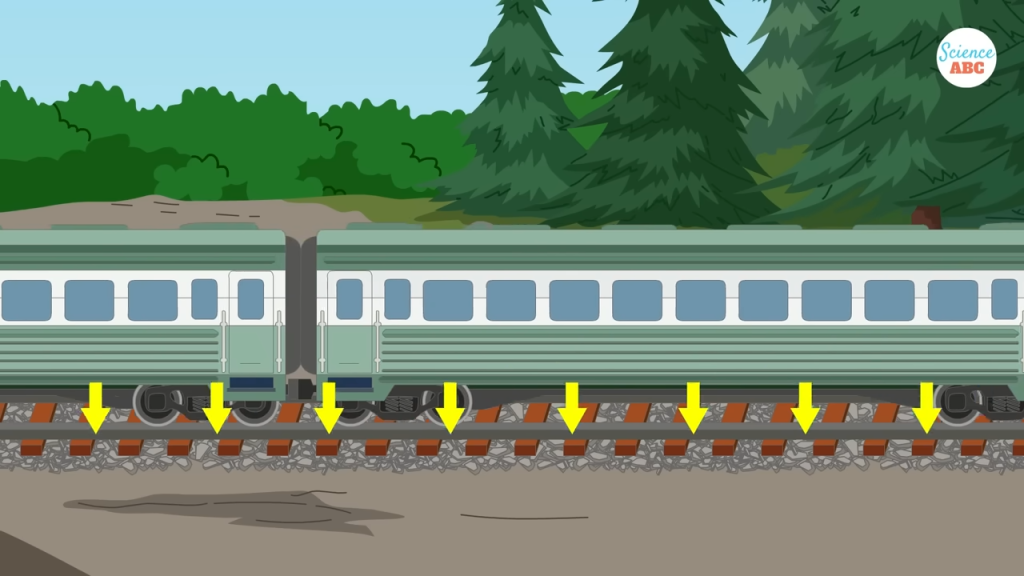

The jagged edges of the stones interlock, forming a solid base that effectively distributes the immense pressure of passing trains. This prevents excessive stress on specific areas, thereby reducing the risk of track deformation or failure.
3. Dampening Vibrations

When trains travel at high speeds, they generate significant vibrations, which can lead to mechanical wear and discomfort for passengers. Track ballast acts as a shock absorber, mitigating vibrations and improving ride quality.
4. Ensuring Proper Drainage
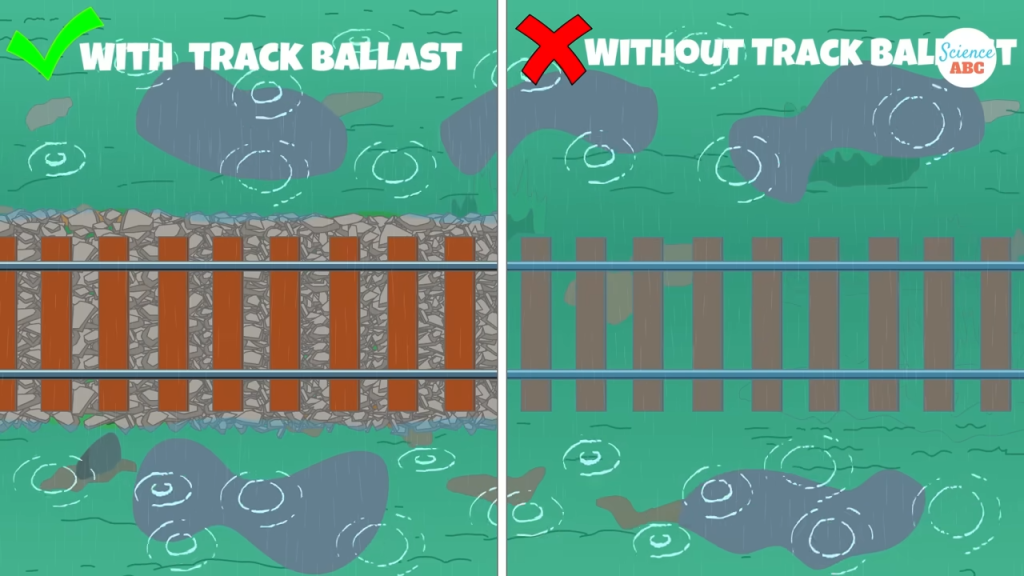
A critical function of ballast is to prevent water accumulation on railway tracks. If water were to pool around the sleepers, it could lead to rapid rusting and degradation of the track’s metallic components. The ballast allows rainwater to drain away efficiently, keeping the railway dry and functional.
5. Preventing Vegetation Growth
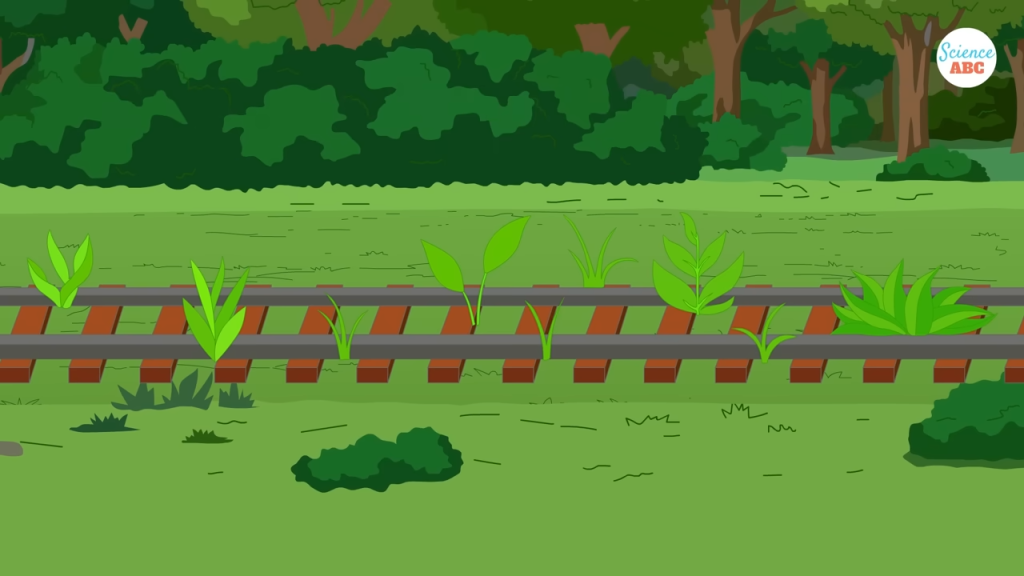

Vegetation such as weeds, grass, and tree roots can severely compromise the stability of railway tracks by causing structural disruptions. The stones in the track ballast create a hostile environment for plant growth, keeping the railway clear of unwanted vegetation.
6. Reducing Noise Pollution

A moving train generates considerable noise, especially for those outside the train. The ballast stones provide a larger surface area for absorbing sound, helping to dampen noise pollution and making rail travel more environmentally friendly.
7. Controlling Heat Expansion

Railway tracks are subject to thermal expansion due to fluctuating temperatures, especially during summer. Track ballast helps mitigate the expansion effects by allowing controlled movement of the track, preventing buckling or warping.
Maintenance of Track Ballast
While track ballast provides numerous benefits, it requires regular maintenance to remain effective. Over time, dirt, debris, and mud can accumulate between the stones, reducing their drainage capabilities. If left unattended, this buildup can weaken the track’s foundation, leading to potential derailments or track failures.
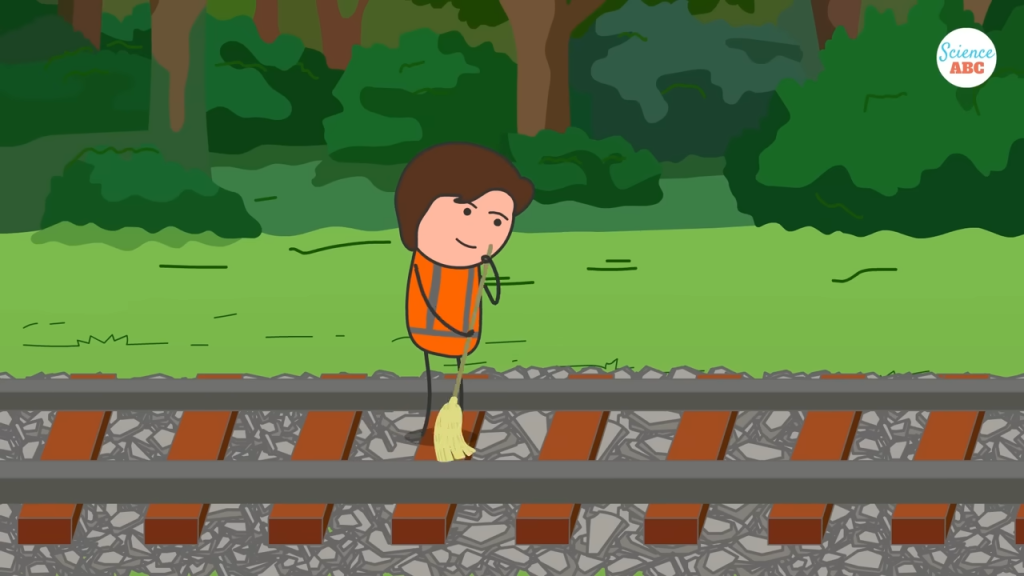

To maintain track quality, specialized ballast cleaners are used to remove dirt and restore the integrity of the stones. Additionally, old or degraded ballast is periodically replaced with new crushed stones to maintain track stability and efficiency.
Conclusion
Though they may seem like simple rocks, track ballast is the unsung hero of railway infrastructure. These carefully chosen stones stabilize the tracks, absorb shocks, prevent vegetation growth, and manage drainage, all while enhancing passenger comfort and safety. Without them, the modern railway system would struggle to function reliably. Next time you take a train journey, take a closer look at those unassuming stones—they are the foundation of rail transport worldwide.



