In today’s fast-paced manufacturing world, companies need speed, precision, and adaptability more than ever. Low volume injection molding has become a preferred solution for businesses that require small to medium production runs of high-quality plastic parts without the expense and lead times of traditional high-volume manufacturing.
Whether for prototyping, pilot production, or specialty product lines, low-volume injection moulding service provides a cost-effective, reliable, and fast way to bring products from concept to market.
This article explores the advantages, process, materials, applications, and considerations of low volume injection molding, showing why it has become an essential tool for modern manufacturing.

What Is Low Volume Injection Molding?
Low volume injection molding is the production of limited quantities of plastic parts, typically ranging from a few dozen to several thousand units. Unlike high-volume production that relies on expensive steel molds, low volume injection molding often uses aluminum molds or rapid tooling, which are faster and more cost-efficient to produce.
This approach is ideal for:
- Functional prototypes
- Pilot production runs
- Market testing of new products
- Specialized or customized components
Low volume injection molding bridges the gap between prototyping and full-scale production, providing functional, high-quality parts quickly.
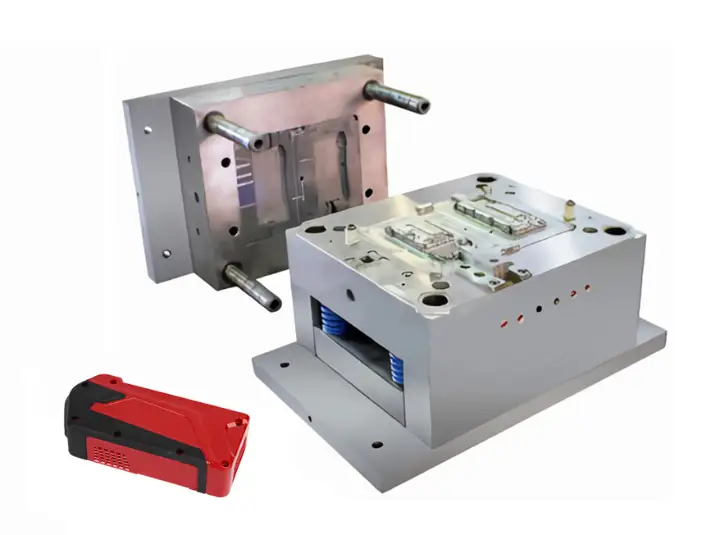

Benefits of Low Volume Injection Molding
1. Cost-Efficient Production
Using aluminum molds or rapid tooling significantly reduces upfront costs compared to steel molds. Businesses can produce high-quality parts without the financial burden of traditional injection molding.
2. Shorter Lead Times
Low volume injection molding enables faster production cycles, allowing manufacturers to test designs, validate parts, and launch products quickly.
3. High Precision and Consistency
Despite smaller production runs, this method delivers tight tolerances, consistent quality, and smooth surface finishes, making parts suitable for functional testing or even end-use applications.
4. Design Flexibility
Aluminum molds or rapid tooling allow quick modifications, enabling designers to iterate and refine products without significant additional cost.
5. Scalable Production
Parts produced via low volume injection molding can later transition to high-volume production, as the material, dimensions, and tooling parameters have already been validated.

Materials Used in Low Volume Injection Molding
Choosing the right material is crucial to ensure functionality, durability, and aesthetics. Common options include:
- Polypropylene (PP): Lightweight, flexible, and chemical-resistant.
- Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS): Rigid, strong, and impact-resistant.
- Polycarbonate (PC): Transparent and durable, ideal for housings.
- Polyethylene (PE): Affordable and flexible for simple components.
- Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA): Clear and glossy, perfect for displays and visual parts.
- Engineering Plastics: Nylon (PA), Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS), and others for high-performance applications.
Selecting the right material ensures that low volume molded parts meet functional and aesthetic requirements, closely matching final production standards.

The Low Volume Injection Molding Process
The process is similar to traditional injection molding but optimized for speed and flexibility:
1. CAD Design
Engineers create a 3D CAD model specifying dimensions, tolerances, and key features. Design optimization ensures manufacturability and part performance.
2. Tooling
Aluminum molds or rapid tooling are manufactured quickly, allowing low volume production without the cost of hardened steel molds.
3. Material Injection
Plastic pellets are melted and injected into the mold under high pressure, filling the cavities completely to produce accurate, repeatable parts.
4. Cooling and Ejection
The molten plastic solidifies in the mold. Finished parts are ejected and may undergo trimming or minor finishing.
5. Quality Checks
Parts are inspected for dimension accuracy, functionality, and surface quality, ensuring they meet project requirements.

Applications of Low Volume Injection Molding
Low volume injection molding is used across industries that require flexibility, precision, and short production runs:
1. Product Development
- Functional prototypes for testing
- Pilot production to gauge market response
- Early iterations to refine design
2. Consumer Electronics
- Device housings, panels, and connectors
- Short production batches for specialized products
3. Automotive Industry
- Interior trim, clips, and connectors
- Limited production parts for niche vehicles or testing
4. Medical Devices
- Surgical instrument prototypes
- Device housings for regulatory testing
- Short-run production for niche medical applications
5. Industrial Machinery
- Custom or replacement parts
- Small batch functional components for specialized equipment

Choosing the Right Low Volume Injection Molding Provider
When selecting a provider, consider:
- Tooling Options: Aluminum molds or rapid tooling for faster production.
- Material Expertise: Ability to handle required plastics for durability and performance.
- Design Support: Assistance with optimizing parts for molding.
- Quality Control: Inspection and testing to ensure consistent output.
- Lead Time: Capability to meet tight schedules and support design iterations.
- Cost Efficiency: Affordable solutions for low-to-medium production volumes.
A reliable provider should also offer technical support, prototyping guidance, and scalability for future high-volume production.
Advantages of Working with Professionals
Partnering with an experienced low volume injection molding service provides:
- Rapid prototyping and validation
- Cost-effective small batch production
- High-quality, functional parts for testing or early market release
- Design flexibility for iteration
- Smooth transition to high-volume production
These advantages make low volume injection molding ideal for startups, R&D teams, and niche manufacturers.
Trends in Low Volume Injection Molding
- Rapid Tooling & 3D Printing: Faster, more affordable mold creation.
- Sustainable Plastics: Use of recycled and eco-friendly materials.
- Micro-Molding: Precision small parts for medical and electronics applications.
- Overmolding & Multi-Material: Combining materials for functional prototypes.
- Automation & Smart Manufacturing: Robotics and IoT improve efficiency, accuracy, and consistency.
These trends reflect a growing demand for speed, flexibility, and sustainability in modern production.

Conclusion
Low volume injection molding provides a flexible, fast, and cost-effective solution for producing small to medium quantities of high-quality plastic parts. It enables businesses to:
- Validate designs quickly
- Produce functional prototypes and pilot batches
- Reduce tooling costs
- Launch products faster and iterate efficiently
- Prepare for high-volume production with minimal risk
For industries such as consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, and industrial machinery, low volume injection molding ensures precision, reliability, and adaptability. By partnering with a professional service provider, companies can bring products from concept to production efficiently, maintaining a competitive edge in today’s market.