What Is Anxiety in Children?
Childhood anxiety is a psychological state of heightened worry, fear, or nervousness, often without a clear external cause. It’s common in children aged 6–10 as they transition into a structured school environment. Unlike short-term fear, anxiety tends to be persistent and can impact daily behavior, academic performance, and relationships with peers or adults.
Types of anxiety typically observed in children include:
- Situational anxiety: Appears in response to specific triggers like tests, public speaking, or separation from parents.
- Trait anxiety: A more stable characteristic where the child is generally more prone to anxiety regardless of the situation.
- Social anxiety: Fear of being judged or rejected, especially in group settings or when speaking in class.
In most primary school environments, situational anxiety is most common, but it can develop into chronic forms without proper support.
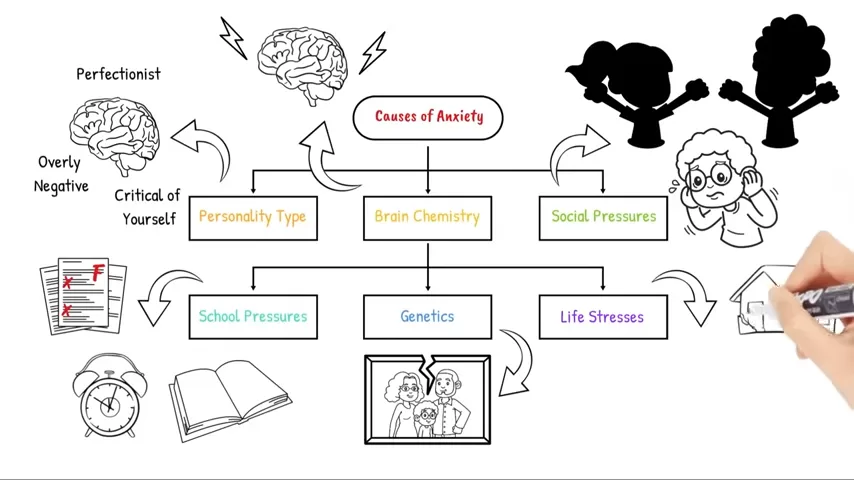
Key Causes of School Anxiety
Several internal and external factors contribute to the development of anxiety in children:
- Academic pressure: Expectations to perform well, fear of making mistakes or getting low grades.
- Family environment: Conflicts at home, overprotective parenting, or lack of emotional support.
- Teacher-student interaction: Strict, critical, or indifferent teachers may unintentionally increase anxiety levels.
- Peer relations: Bullying, exclusion, or lack of social skills can lead to isolation and anxiety.
- Low self-esteem: Children unsure of their abilities or who receive little positive reinforcement may begin to doubt themselves.
How to Recognize Anxiety in a Child
Some of the common behavioral and physical signs of anxiety in schoolchildren include:
- Avoiding tasks or participation in class, even if the child knows the material.
- Excessive worrying about small things (e.g., being late, forgetting homework).
- Physical complaints such as stomachaches, headaches, or fatigue before school.
- Tantrums, crying, or panic attacks in anticipation of school-related events.
- Trouble sleeping, nail-biting, or repetitive habits.
- Clinginess, particularly during school drop-offs.
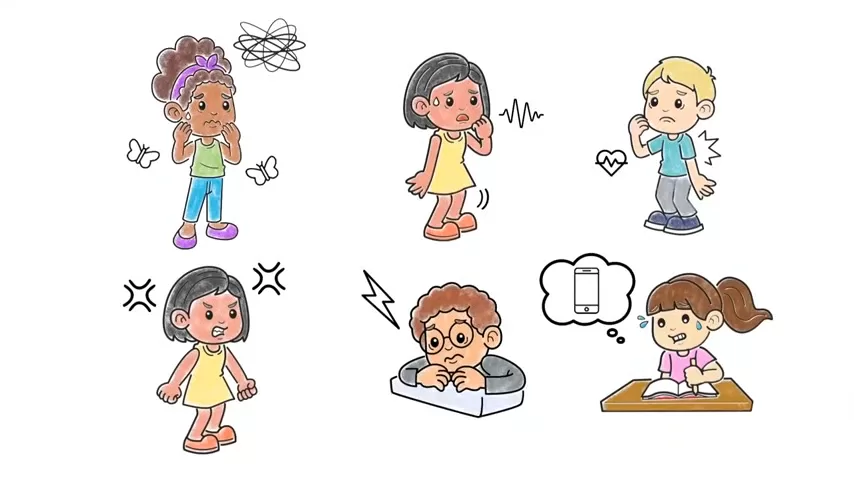
Recognizing these signs early helps prevent more serious psychological consequences later in life.
Psychological Strategies to Reduce Anxiety
Several practical and psychological techniques have been proven effective in managing anxiety among schoolchildren:
- Play therapy: Allows children to express emotions through drawing, games, or role-play, making it easier to address fears.
- Breathing exercises: Help regulate nervous system responses and reduce physical symptoms of anxiety.
- Emotion cards or “worry boxes”: Children write or draw their worries and “store” them in a symbolic container.
- Visualization and mindfulness: Simple imagery exercises like imagining a safe space can reduce stress responses.
- Positive reinforcement: Acknowledging efforts rather than just outcomes helps build confidence.
Teachers and psychologists often combine several of these techniques for a holistic approach.
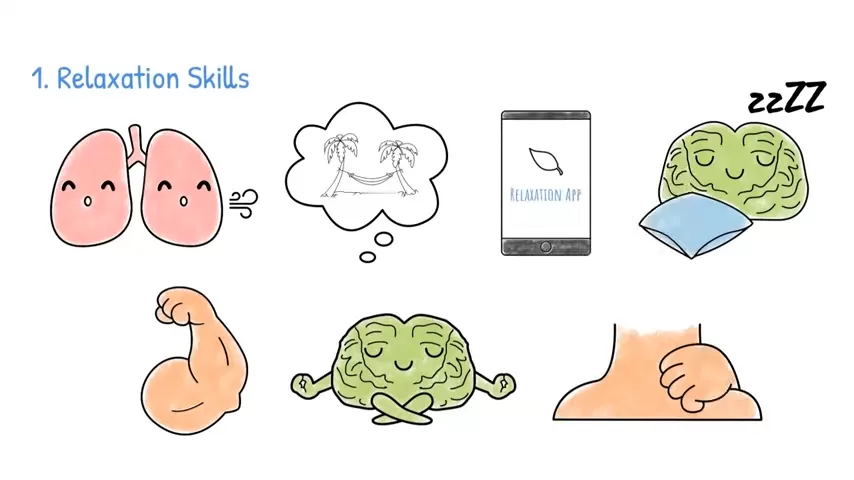

The Role of the Teacher and School Environment
Teachers are key figures in a child’s psychological world during school years. Their tone of voice, body language, and response to mistakes can either alleviate or amplify anxiety. Effective teachers create a safe, respectful, and predictable environment, where students know what to expect and feel emotionally supported.
Some classroom strategies that help reduce anxiety:
- Using non-verbal cues to support rather than shame students.
- Providing flexible response options (e.g., written answers instead of oral if anxiety is high).
- Avoiding sarcasm or comparison between students.
- Fostering collaboration over competition.
Regular communication with parents can also help identify underlying issues and align support across home and school.
Involving Parents in Anxiety Reduction
Parents play a critical role in supporting their child’s emotional well-being. To reduce school anxiety, it’s important they:
- Refrain from punishing or dismissing fears (“Don’t be silly” or “You’re overreacting”).
- Avoid passing their own anxieties onto the child.
- Model calm behavior and healthy coping mechanisms.
- Encourage effort over perfection.
- Celebrate small achievements consistently.
If anxiety seems persistent or worsening, professional counseling may be necessary.

Real-World Case Example
At a public primary school in Eastern Europe, a group of 2nd-grade students took part in a two-month intervention program that included:
- Weekly group sessions on emotional intelligence.
- Daily breathing rituals before morning lessons.
- Expressive art therapy sessions after stressful events (like math quizzes).
By the end of the term, over 80% of students self-reported lower stress levels, and teachers noted fewer disruptions, more classroom participation, and improved peer relationships.
Long-Term Impact of Childhood Anxiety
If left unaddressed, school anxiety can evolve into more serious mental health issues in adolescence and adulthood, including depression, panic disorders, or social phobia. It may also affect academic performance, social development, and self-identity.
Intervening early, recognizing signs, and offering consistent emotional support can drastically change a child’s developmental trajectory.
Conclusion
Anxiety in primary school children is both a common and serious issue, often misunderstood or overlooked. With the right combination of teacher awareness, parental involvement, and psychological support techniques, it is possible to not only manage but significantly reduce anxiety in the early years. Drawing on insights like those presented in https://moluch.ru/archive/308/120173/, we gain a clearer picture of what these children face — and how we can help.