The human body and mind possess abilities that remain largely unexplained despite extensive research. From extraordinary memory recall to unusual sensory experiences, these capabilities challenge our understanding of science, neurology, and human potential. Here are ten human capabilities that continue to fascinate and perplex scientists.
1. Perfect Pitch
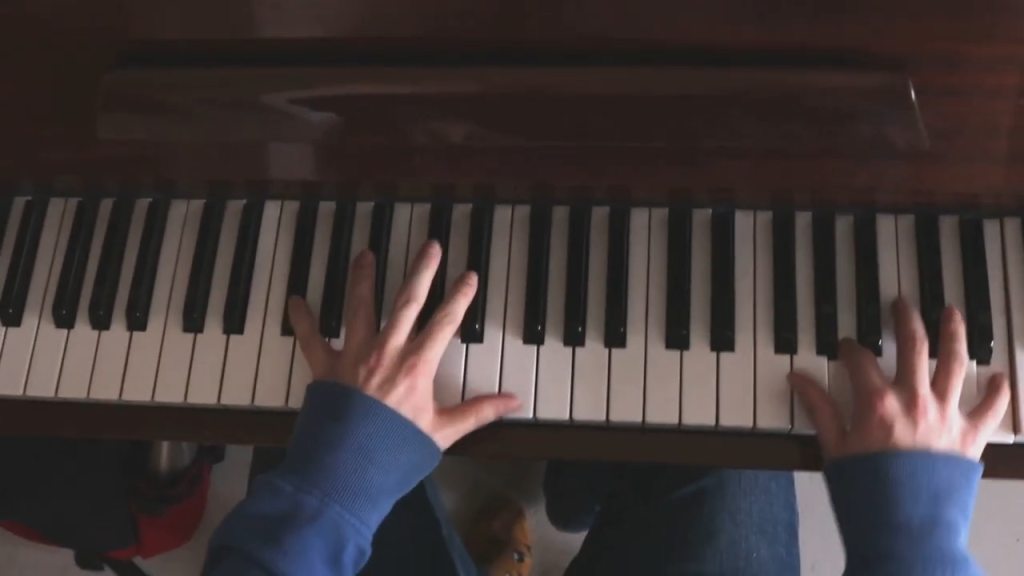

Perfect pitch, also known as absolute pitch, is the rare ability to identify or produce a musical note without a reference tone. People with this skill can name a note from a car horn or sing an exact pitch without external cues. Scientists have debated whether it is genetically inherited or developed through early musical exposure. Interestingly, it is more prevalent in tonal language speakers like Mandarin. Despite ongoing research, the exact neural mechanisms that enable perfect pitch remain unclear.
2. Synesthesia
Synesthesia is a neurological phenomenon where the stimulation of one sensory pathway leads to involuntary experiences in another. A common example is grapheme-color synesthesia, where letters or numbers appear as specific colors. This cross-wiring of the brain is thought to result from unusual neural connections, often running in families. However, the precise reason why some individuals experience synesthesia while others do not is still a mystery.
3. Savant Syndrome

Savant syndrome is a rare condition where individuals with developmental disorders, such as autism, exhibit exceptional talents in areas like math, music, or art. Some can solve complex calculations instantly or recreate entire landscapes from memory. One theory suggests that their brains compensate for cognitive impairments by enhancing other areas, but the exact cause remains unknown. Research into savant syndrome could unlock new insights into human intelligence and brain plasticity.
4. Photographic Memory

Photographic or eidetic memory allows individuals to recall images, sounds, or objects in extreme detail after only brief exposure. Unlike normal memory, which is often reconstructive and subject to distortion, eidetic memory seems to store and retrieve information with remarkable accuracy. Brain imaging studies have suggested heightened activity in regions associated with visual perception and memory, yet the true nature of this ability remains debated.
5. Superhuman Strength
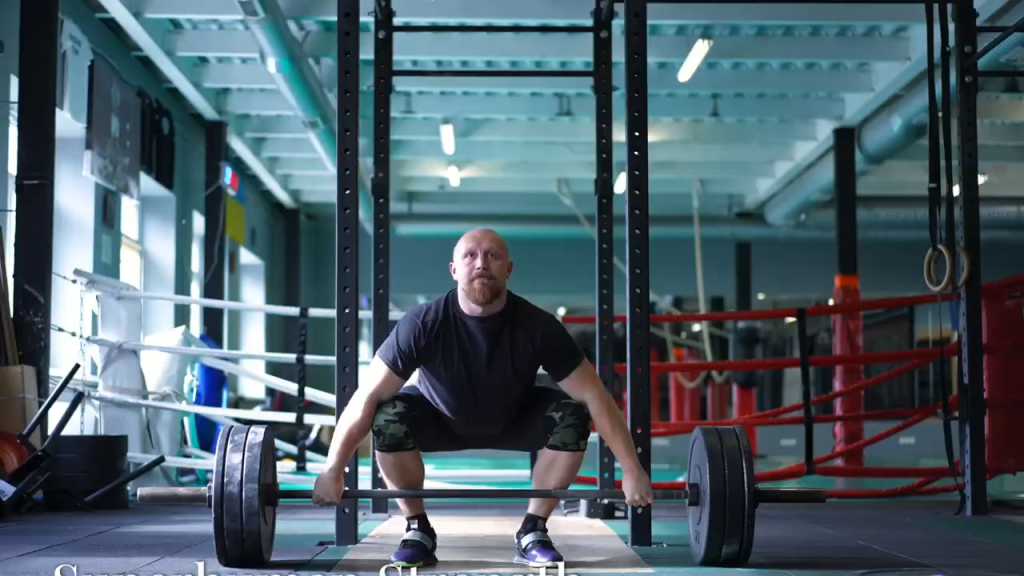

There have been numerous accounts of people exhibiting extreme strength in life-or-death situations, such as lifting cars to save loved ones. Known as hysterical strength, this phenomenon is believed to result from an adrenaline surge that temporarily enhances muscle function. However, scientists still don’t fully understand why only certain individuals experience it, or how the body regulates such bursts of power under normal circumstances.
6. Intuition

Intuition, often described as a gut feeling or sixth sense, allows people to make decisions seemingly without logical reasoning. Some researchers believe it stems from the brain’s ability to rapidly recognize patterns and process information subconsciously. Brain regions like the amygdala and hippocampus may play a role, but the exact mechanisms behind intuitive decision-making remain unclear.
7. Exceptional Longevity

While the average human lifespan continues to rise, some individuals, known as super-agers, live past 100 years with sharp cognitive abilities and relatively good health. Scientists have studied populations with high numbers of centenarians, such as those in Okinawa, Japan, to understand the factors contributing to longevity. While genetics, diet, and lifestyle play roles, the exact biological mechanisms that promote exceptional longevity remain a puzzle.
8. Hyperthymesia (Superior Autobiographical Memory)

People with hyperthymesia can recall nearly every event of their lives with astonishing clarity, down to specific dates and details. Studies show that individuals with hyperthymesia have larger-than-average temporal lobes and caudate nuclei, brain regions linked to memory storage and habit formation. However, scientists still don’t know why only a handful of people develop this ability.
9. Out-of-Body Experiences (OBEs)

Some people report perceiving themselves as being outside their physical body, often floating above themselves and observing their surroundings. OBEs can occur during near-death experiences, meditation, or under the influence of certain substances. Research suggests that OBEs may be linked to disturbances in the brain’s temporoparietal junction, but their realism and vividness remain scientifically unexplained.
10. Pain Insensitivity
Pain insensitivity, or congenital analgesia, is a rare condition where individuals do not feel physical pain despite severe injuries. While this might seem advantageous, it poses serious risks, as affected individuals may suffer unnoticed wounds or broken bones. Scientists have linked congenital analgesia to mutations in specific genes affecting nerve signal transmission, yet the full biological mechanisms remain unknown.
Final Thoughts
Human capabilities often push the boundaries of scientific understanding, revealing the incredible complexities of the brain and body. As research progresses, we may uncover the mechanisms behind these extraordinary abilities, potentially unlocking new frontiers in neuroscience, medicine, and human potential. Until then, these mysteries continue to fascinate and challenge scientists worldwide.



